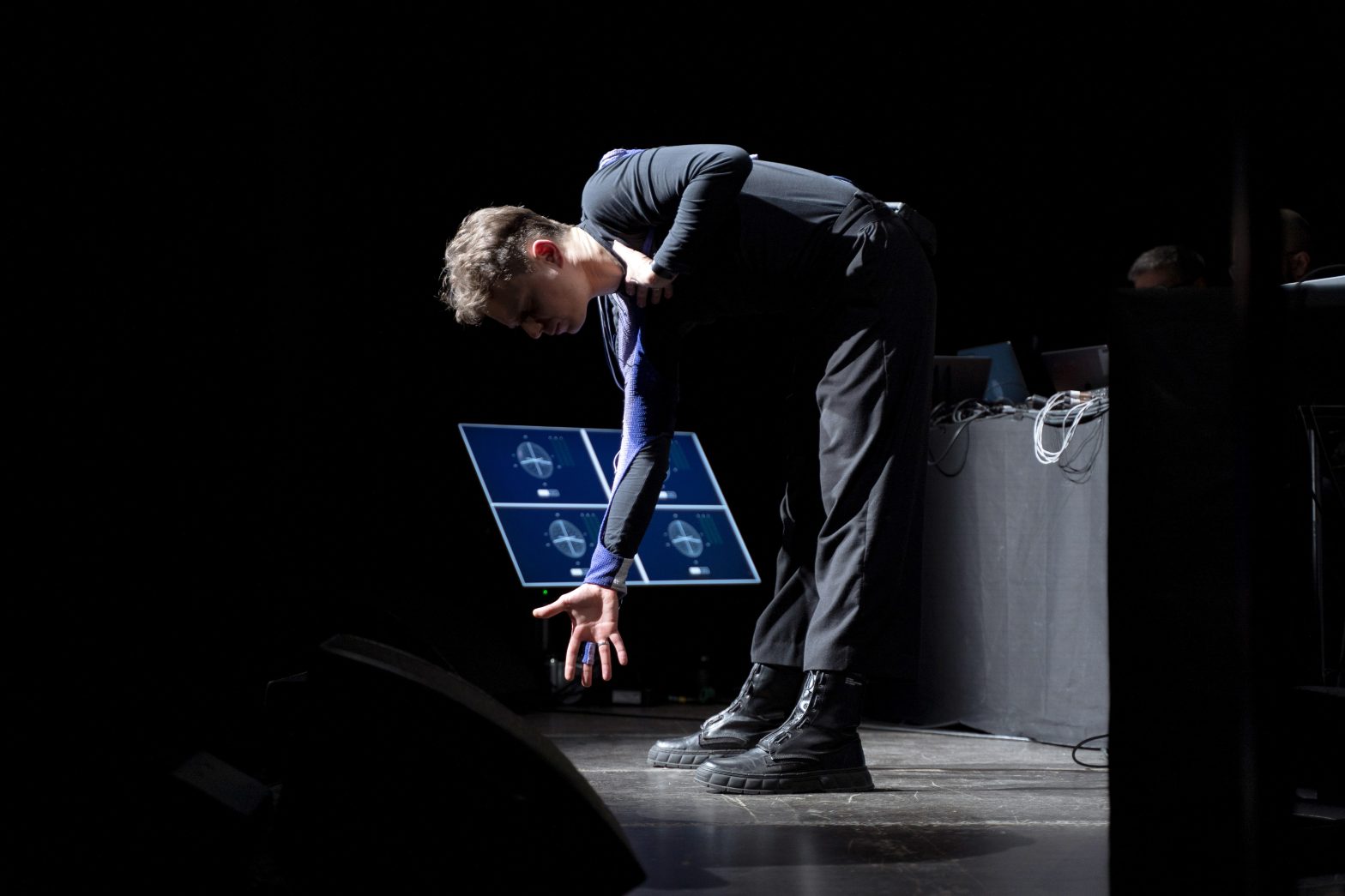
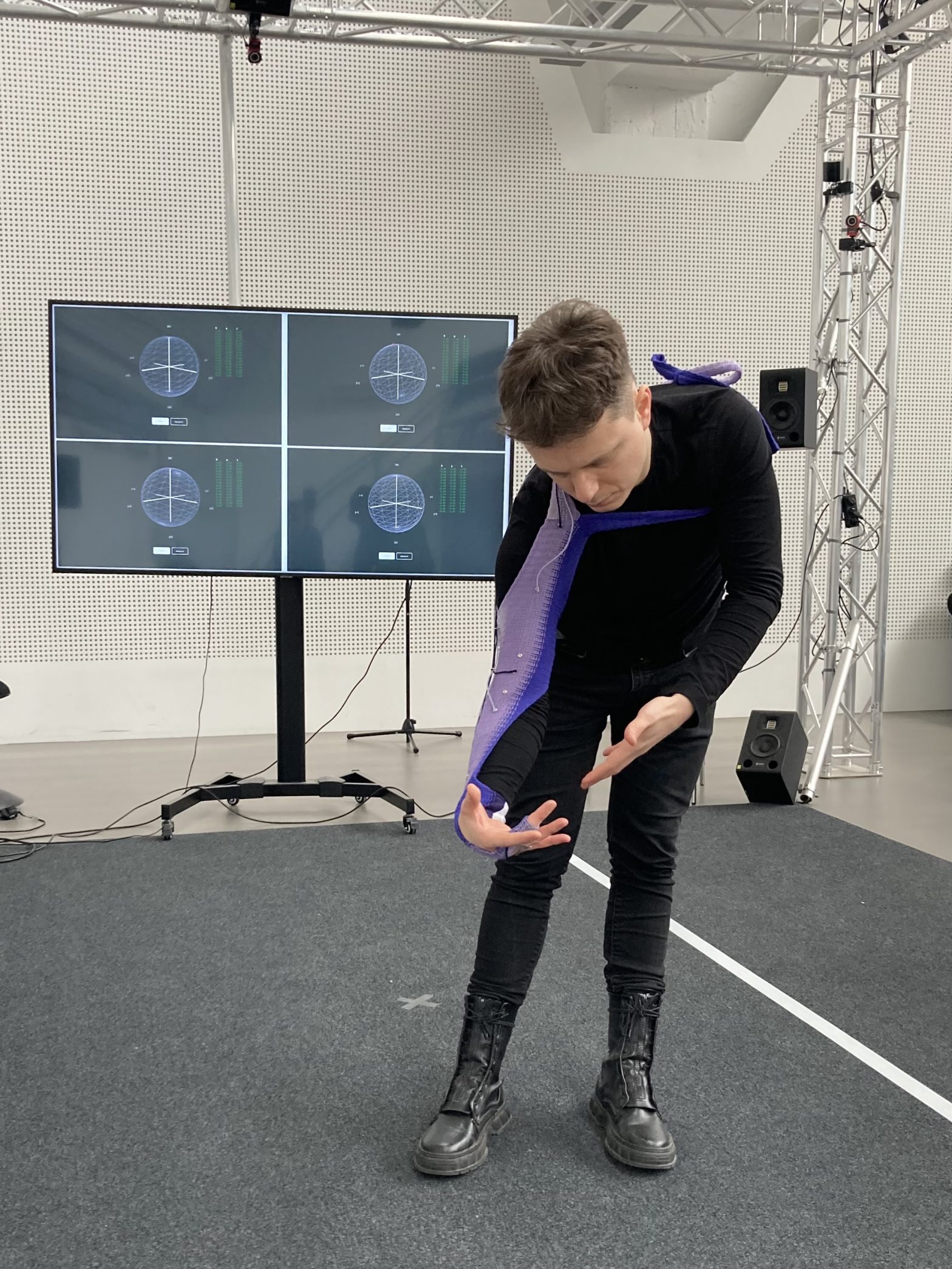
-
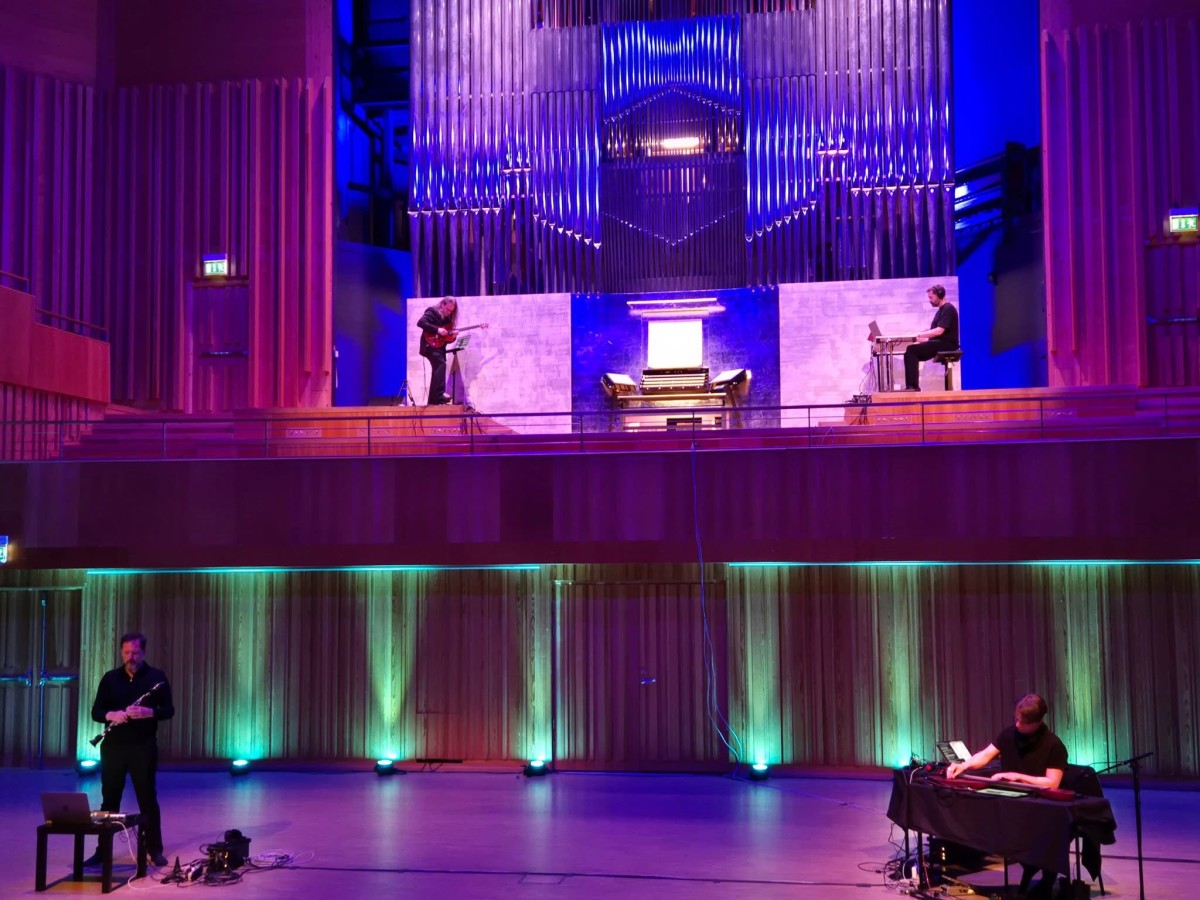

TCP/Indeterminate Place quartet performs Reconciliation at Studio Acusticum
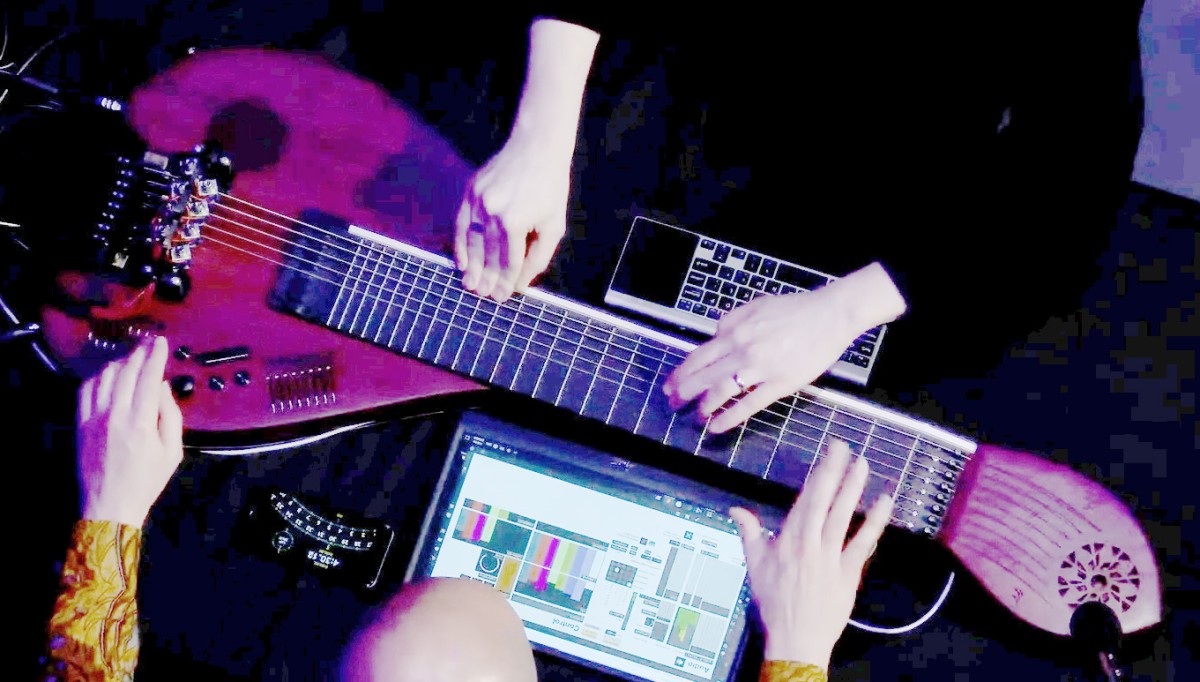
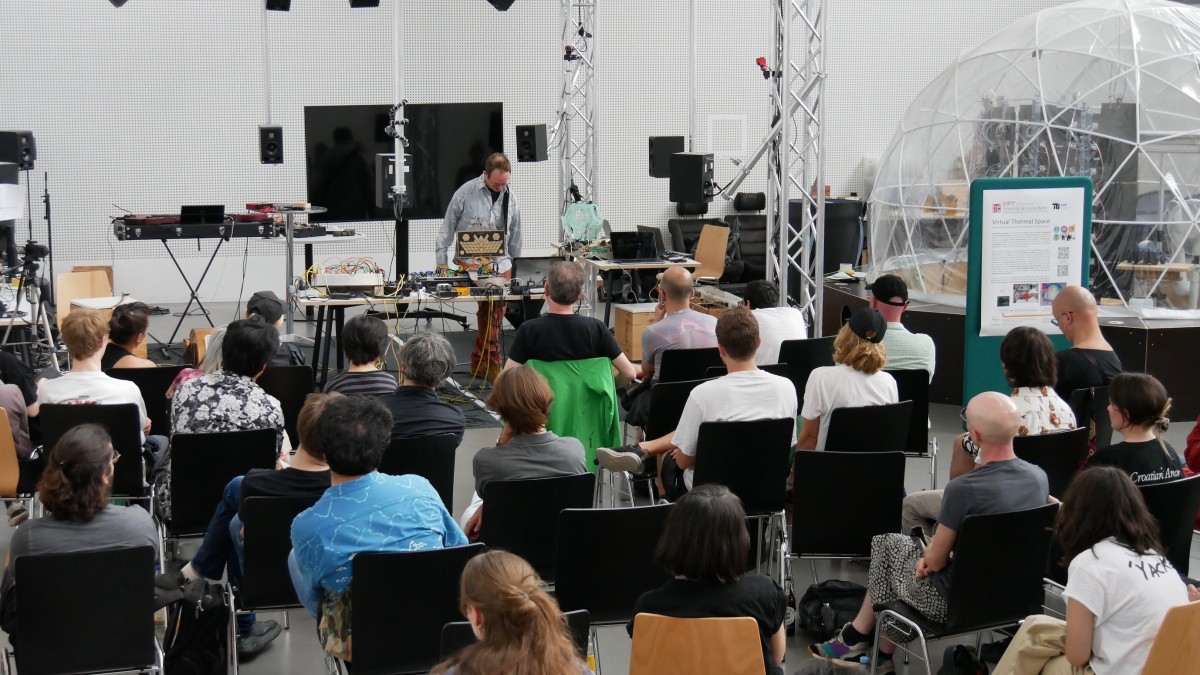
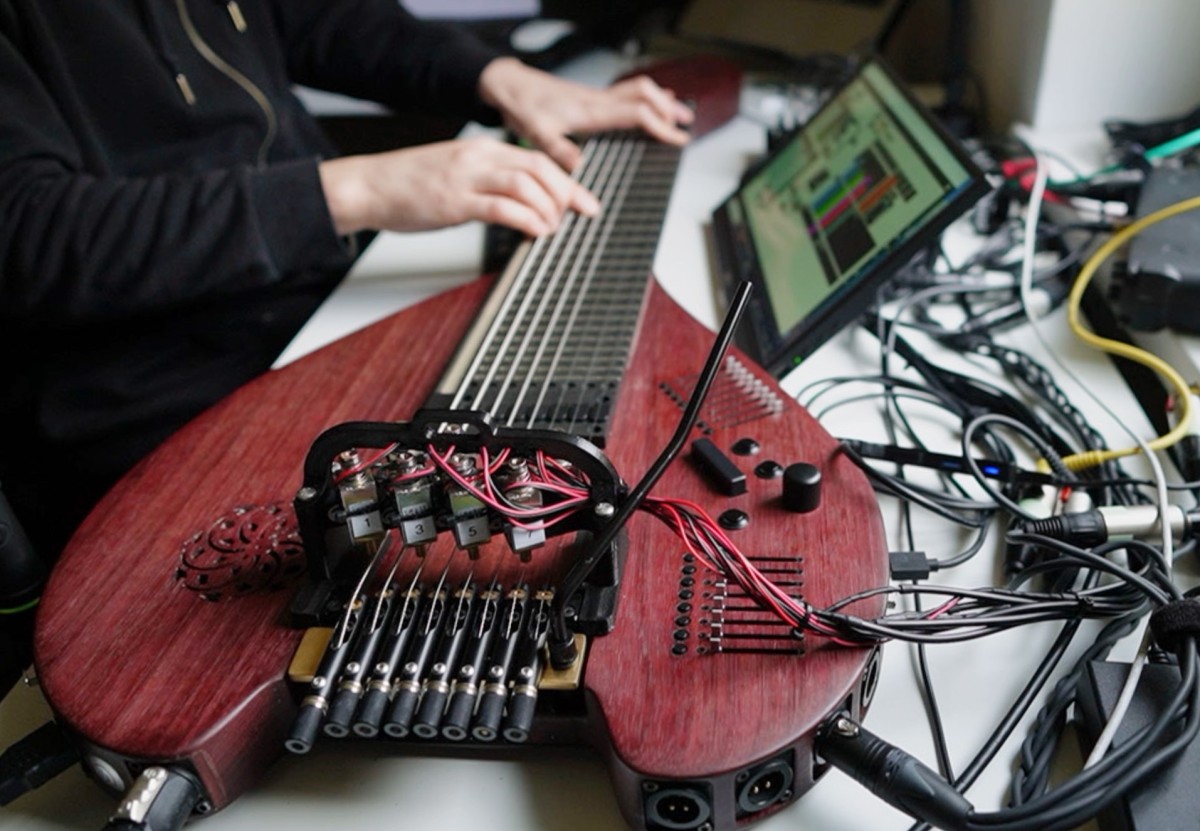
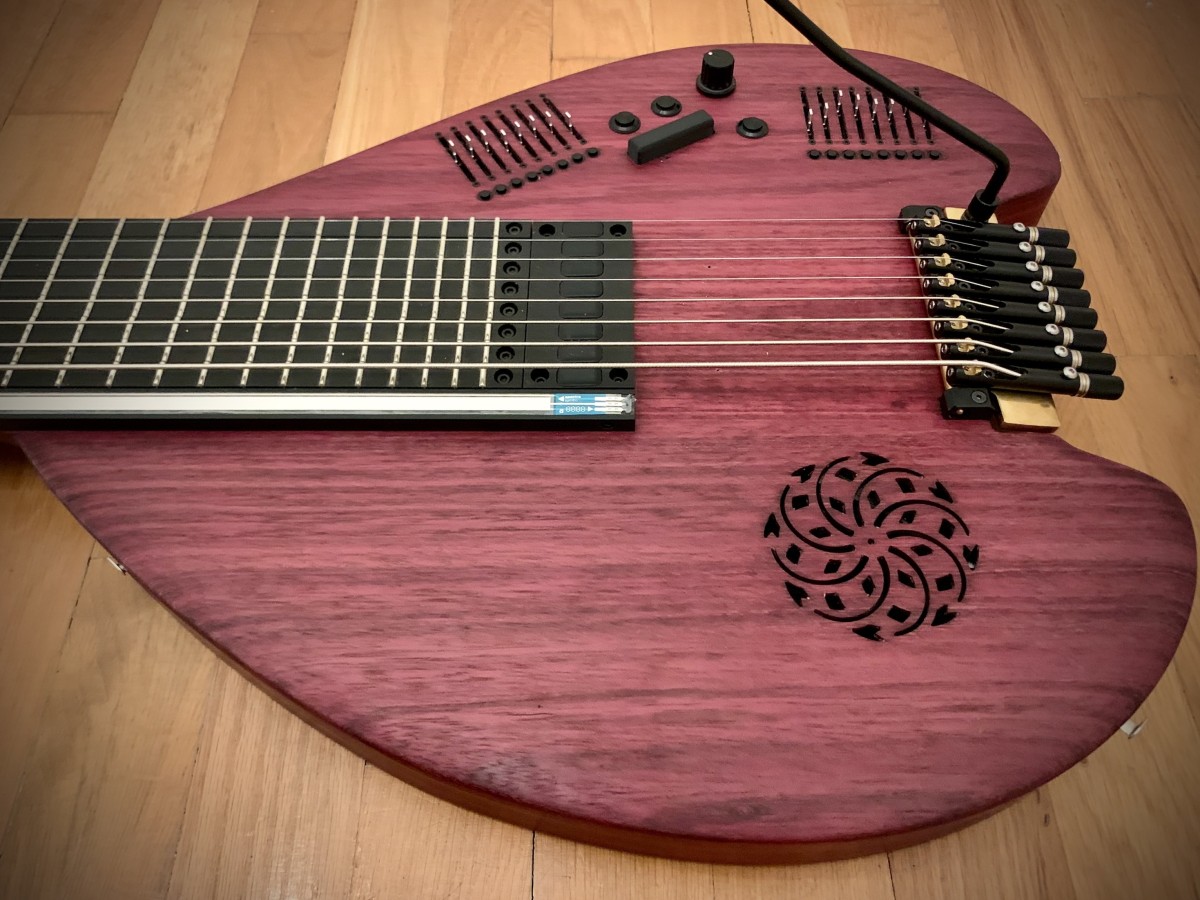
On Monday 9 June 2025 the TCP/Indeterminate Place quartet performed Reconciliation, a piece we composed in 2024 for a special double duo telematic performance in which two of us performed at the Kapelle der Versöhnung in Berlin and the other two at the Orgelpark in Amsterdam. This time we were all at the Studio Acusticum…